Using Headless Marketing API
Now you have installed and setup the uMarketingSuite Headless API we can jump in and learn about how to use it.
Summary
Out of the box uMarketingSuite segmented content and A/B tests will work out of the box with Umbraco's Content Delivery API and return the correct content to the user and we suggest you refer to Umbraco's official documentation in order to understand how to use and query content from Umbraco.
In order to track a user to the site and potentially place them into a segment and associate a persona, we will need to track which pages the visitor is viewing and this needs to be done by making a HTTP POST request to the /umbraco/umarketingsuite/api/v1/analytics/pageview/trackpageview/client endpoint with the following JSON body to indicate what page the user has visited.
{
"url": "https://localhost:44374"
}
The logic in uMarketingSuite will determine if the user has met any thresholds to put them into a segment, into an A/B test or any personalization should be applied and subsequent requests to the Umbraco content API can then deliver the personalised content.
Why does uMarketingSuite need to be explicitly notified?
As we can't assume a single request to the Umbraco Content Delivery API means one page visit.
Configuration
The settings for uMarketingSuite Headless package can be configured via .NET Options be it with an AppSettings JSON file, Environment Variables or some other configuration source.
Below is an example of configuration values used in AppSettings.json which if you use a modern IDE such as Visual Studio or JetBrains Rider then you will get auto completions on the available settings uMarketingSuite.Headless package offers you.
"uMarketingSuite": {
"DeliveryApi": {
"Segmentation": {
"ContentById": true,
"ContentByIds": true,
"ContentByPath": true,
"ContentByQuery": true
}
}
}
The values are watched by .NET so these can be changed at runtime without having the website to be restarted for these changes to configuration to take effect.
| Key | Description | Default Value |
| ContentById | Enable Umbraco content delivery API endpoint by ID /umbraco/delivery/api/v1/content/item/{id} |
true |
| ContentByIds | Enable Umbraco content delivery API endpoint that uses an array of IDs /umbraco/delivery/api/v1/content/item |
true |
| ContentByPath | Enable Umbraco content delivery API endpoint by Path /umbraco/delivery/api/v1/content/item/{path} |
true |
| ContentByQuery | Enable Umbraco content delivery API endpoint by Query /umbraco/delivery/api/v1/content |
true |
Analytics
/umbraco/umarketingsuite/api/v1/analytics/pageview/trackpageview/client
This request is used to track a page view and requires the url property of the page that a user has visited in the site, optionally the reffererUrl can be set to inform uMarketingSuite where the user came from.
/umbraco/umarketingsuite/api/v1/analytics/pageview/trackpageview/server
This is used as the same above, but is useful when a frontend JAMStack Server such as a NuxtJS server or similar is being used and can notify uMarketingSuite when a page view has taken place and provide us extra information; request headers, browserUserAgent, remoteClientAddress and userIdentifier
Client and Server
uMarketingSuite tries to get a bunch of information about you as a visitor based on your request. It does so by extracting said information from your request, e.g. HTTPContext.
The Client side version is you were to make an API call directly to Umbraco straight from your browser, meaning that all the meta-data about the request is just... your request. Your IP address, your cookies, your request headers, etc...
The Server side version is if you were to have a server in between your browser & Umbraco, like a NuxtJS server, to do the rendering and handling of requests. Because of such a server, each request coming to Umbraco isn't the end-client, but our NuxtJS server, meaning that we wouldn't be tracking the headers, IP addresses etc. from those requests, but from the server instead. Therefor you can use the Server version to add that additional meta-data to your pageview tracking in between the Next.JS server & Umbraco.
Page Events
/umbraco/umarketingsuite/api/v1/analytics/pageevent/trackpageevent
Introduced in version 2.3.0, this request is used to track events. After tracking a pageview using the Analytics TrackPageview API as mentioned above, you will receive both an externalVisitorId & pageviewId. In order to track events, the request requires a supplied pageview-Id header, and a request body containing a category, action (optional), label (optional) and timestamp (optional).
Optionally you can also provide an External-Visitor-Id header in order to automatically update the in-memory visitor to automatically reflect segments involving events for said visitors. Without supplying this parameter, the pageview has to be flushed to the database (as per configuration) before any segment information gets updated (e.g. personalization variants using segments based on events).
Segmentation - Assets
/umbraco/umarketingsuite/api/v1/segmentation/assets/item/{path}
/umbraco/umarketingsuite/api/v1/segmentation/assets/item/{id}
These two requests allow you to see if the content page by its ID or Path has a variant with Javascript or CSS that has been added for you to inject into your page for a
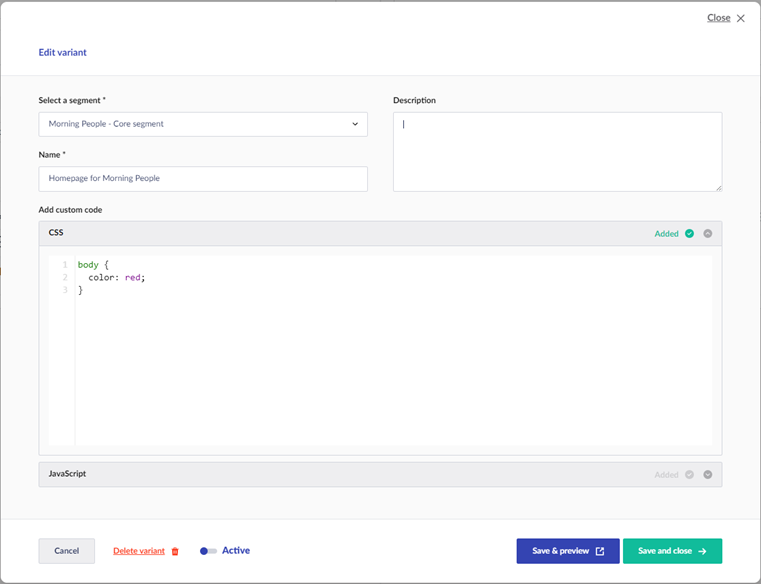
Segmentation - Content
/umbraco/umarketingsuite/api/v1/segmentation/content/segments
/umbraco/umarketingsuite/api/v1/segmentation/content/segments/{path}
/umbraco/umarketingsuite/api/v1/segmentation/content/segments/{id}
These requests return information about which segments (personalization & A/B testing) are configured to be on a page in general. This could be used to know if a page could have content that could change by uMarketingSuite and if not it could perhaps be cached more aggressively.
Segmentation - Visitor
/umbraco/umarketingsuite/api/v1/segmentation/content/activesegments/{path}
/umbraco/umarketingsuite/api/v1/segmentation/content/activesegments/{id}
These requests return the segment (personalization & A/B testing) that the current visitor ID of that specific page belongs to based on its cookie.